Status of the School Canteen in Burundi
This is a guest blog written by Mr. Liboire BIGIRIMANA, National Director of School Canteens in Burundi and Spokesperson for the Ministry of National Education and Scientific Research and Focal Point for Burundi, 2021 Global Survey of School Meal Programs
School canteens in Burundi have been in existence since the 1960s supported by the interventions of the World Food Programme (WFP). WFP supplied schools having boarding facilities with commodities such as powdered milk, meat, and canned fish. In 2008, the northern provinces of Burundi were affected by climate change, in the form of drought, leading to the impoverishment of households. This situation forced children to drop out of school and flee to neighboring countries of Burundi, mainly Tanzania and Rwanda. Others have moved to major cities in Burundi in order to get jobs and earn money.
To remedy this situation, the WFP and the Government of Burundi entered into an agreement to finance hot midday meals to motivate children to return to school for classes.
In 2013, the philosophy of the school canteen changed from being an emergency response to a development intervention. In this new approach, the Government of Burundi decided to develop an endogenous school canteen system known as Home Grown School Feeding, whereby a school canteen obtains local products from small producers grouped into cooperatives and agricultural production associations, thus forming a permanent market with the small producers.
I. Major Achievements of the Government in School Feeding
Several major achievements have been made by the Government of Burundi including:
Institutional aspects
- In 2016, a National Directorate of School Canteens was created and housed institutionally at the Minister’s Cabinet;
- On 14th November 2018, the Government of Burundi validated and endorsed the National School Feeding Program (NSFP), a tool for strategic orientation and dialogue with Development Partners (PTF);
- In 2020, Her Excellency the First Lady of Burundi Mrs. Angéline NDAYISHIMIYE agreed to be the Patron of the National School Feeding Program;
- In 2021, Burundi joined the Global School Meals Coalition.
Regarding financial commitments, since 2008 the Government of Burundi has made its counterpart funds available to WFP to finance the purchase of commodities for the school canteen. The amount allocated to school feeding by the government is about 2 million US dollars. Government contribution is expected to reach 6 million US dollars by the start of the 2023-2024 school year!
A study carried out locally shows that the school canteen contributes to the improvement of school indicators and the standard of living of producers.
II. Geographical Coverage
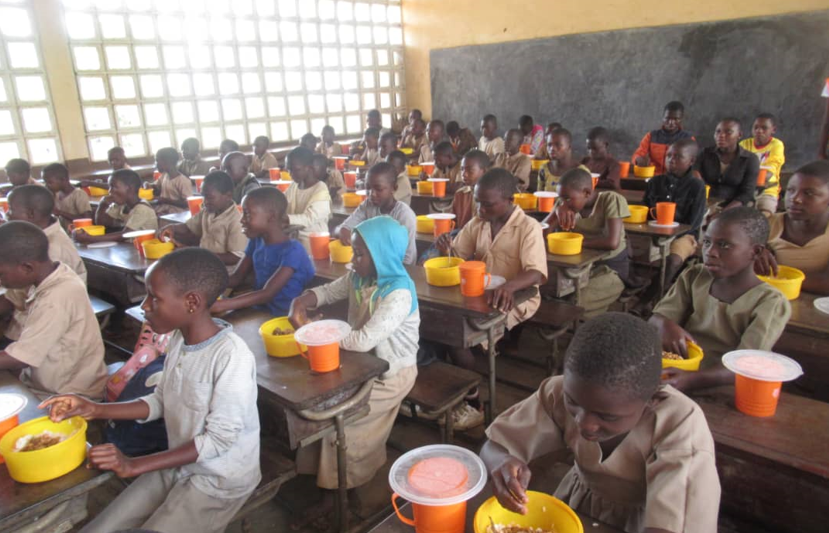
The National School Feeding Program (NSFP) intervenes in 847 elementary schools across 7 provinces of the country namely Bubanza, Bujumbura, Cibitoke, Gitega, Muyinga, Ngozi, and Kirundo provinces. About 650,000 school children out of an estimated target of 2.8 million children in elementary schools benefit from the NSFP. To achieve universal school canteen coverage, a substantial mobilization of funds needs to be done by development partners, the government, and the communities to fill current coverage gaps.
III. Best Practices in School Feeding in Burundi
The implementation of the NSFP faces several challenges, due to, most notably, limited financial resources. In addition, innovations are needed at the canteen level, especially related to the use of firewood and environmental degradation. The school feeding implementers in Burundi are developing best practices, including the following:
a) To limit the volume of firewood to be used, schools considered building improved stoves (i.e. utilizing concrete stoves that use less firewood and conserve heat thereby drastically reducing the quantity of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere), and the use of “briquettes”, fuel obtained following the industrial compaction of household residues, grasses, and rice crop residues
b) For good governance of the school canteen, a stock management tool has been introduced in schools with school canteens known as “School Connect”. This approach utilizes a digital management tool installed on tablets which allows for efficient and effective tracking and management of inventory. The tool provides an idea of the actual use of food in relation to the number of beneficiaries;
c) The consumption of products with very high nutritional value such as mushrooms and milk for a consistent protein intake;
d) The involvement of communities to support the school canteen: communities participate in the preparation and distribution of school meals, provide firewood, water, and vegetables to supplement the children’s food ration;
e) The introduction of decentralized purchases: the Government of Burundi and the WFP provide those in charge of the decentralized structures with the financial means to buy commodities for the canteen directly from food producers. This approach is helps canteens overcome stock-outs, increases the quantities of accessible commodities, and cuts down on the exorbitant cost of transporting food;
f) Introduction of hydroponics, a means of producing vegetables in greenhouses in areas with water deficits to supplement school meals with vegetables.
IV. National School Feeding Program Partners
The implementation of the NSFP is supported by the interventions of various development partners, including the World Bank (construction of improved stoves and their shelters, the supply of funds to buy commodities), the Netherlands, the Global Fund for Education through the French Development Agency (AFD), the Russian Federation, The Rockefeller Foundation (Financial and technical support), the United States of America through the McGovern-Dole Food For Education program. At the local level, the development of the fortified milk and corn flour value chain rose out of local partnership. Successful partner contributions are characterized by success in increased environmental protection, supplying of healthy, rich, and nutritious meals, ensuring the good governance of the school canteen, and more.
V. Participation of Burundi in Global Child Nutrition Forums
Since 2014, Burundi has participated in most of the Global Child Nutrition Forums, organized by the Global Child Nutrition Foundation (GCNF). Burundi has participated in Forums organized in Brazil, Cape Verde, South Africa, Canada, Tunisia, Armenia, and Benin. All these Forums have enabled Burundi to capitalize on the experiences of other countries in the management, financing, and sustainability of school feeding. For example, the Forum held in Brazil helped Burundi draft its school feeding policy. At the Forum held in Montreal, Canada, Burundi was able to build partnerships to finance the school canteens. At the Benin Forum in 2022, Burundi was able to better understand the part each government played in financing its school feeding. This is why, as of September 2023, Burundi will finance school feeding to the tune of 12.7 billion Burundian Francs, i.e. 6 million US dollars, an increase of 164% compared to the financing of previous years (4.8 billion Burundian Francs)!