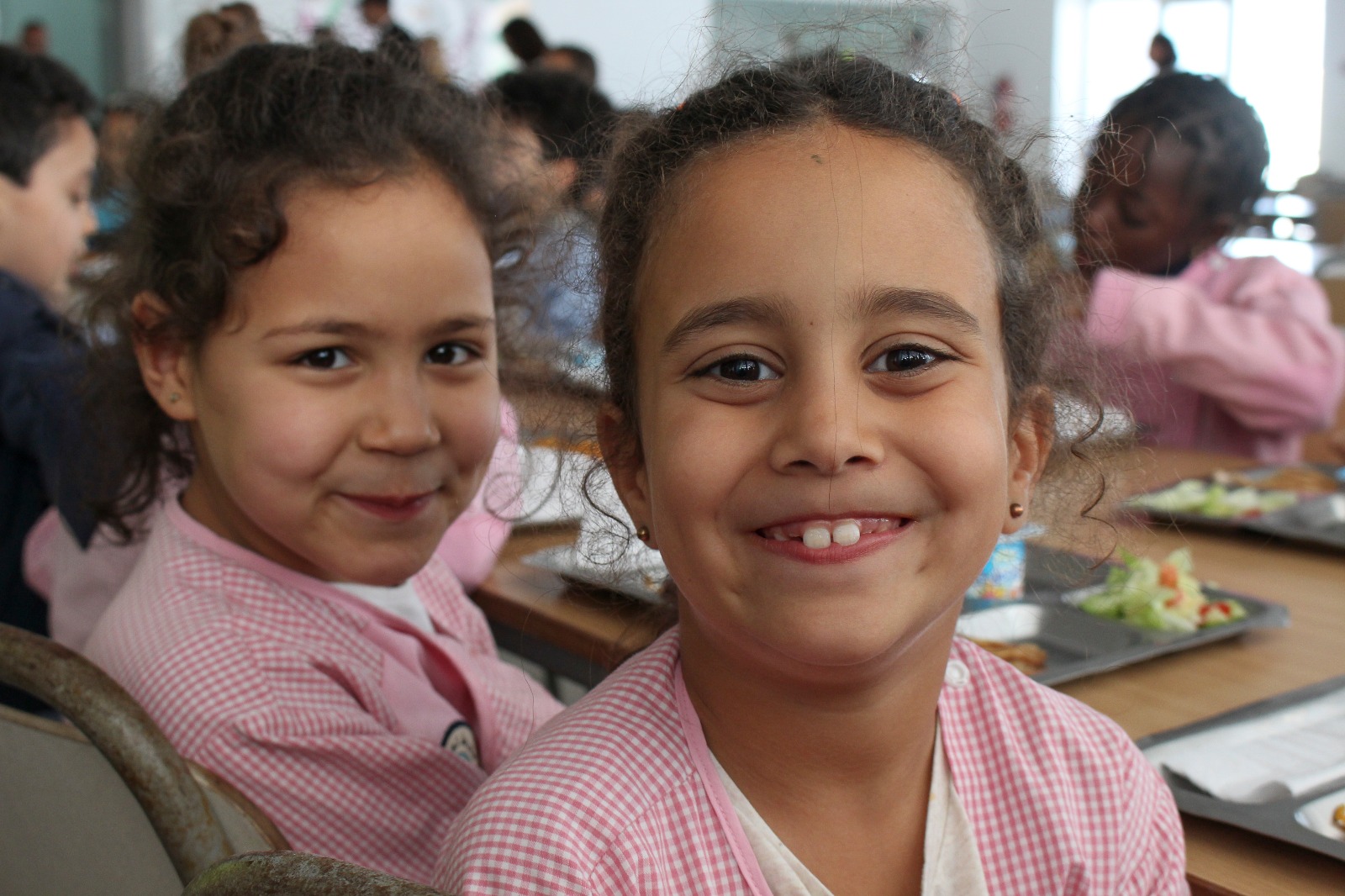
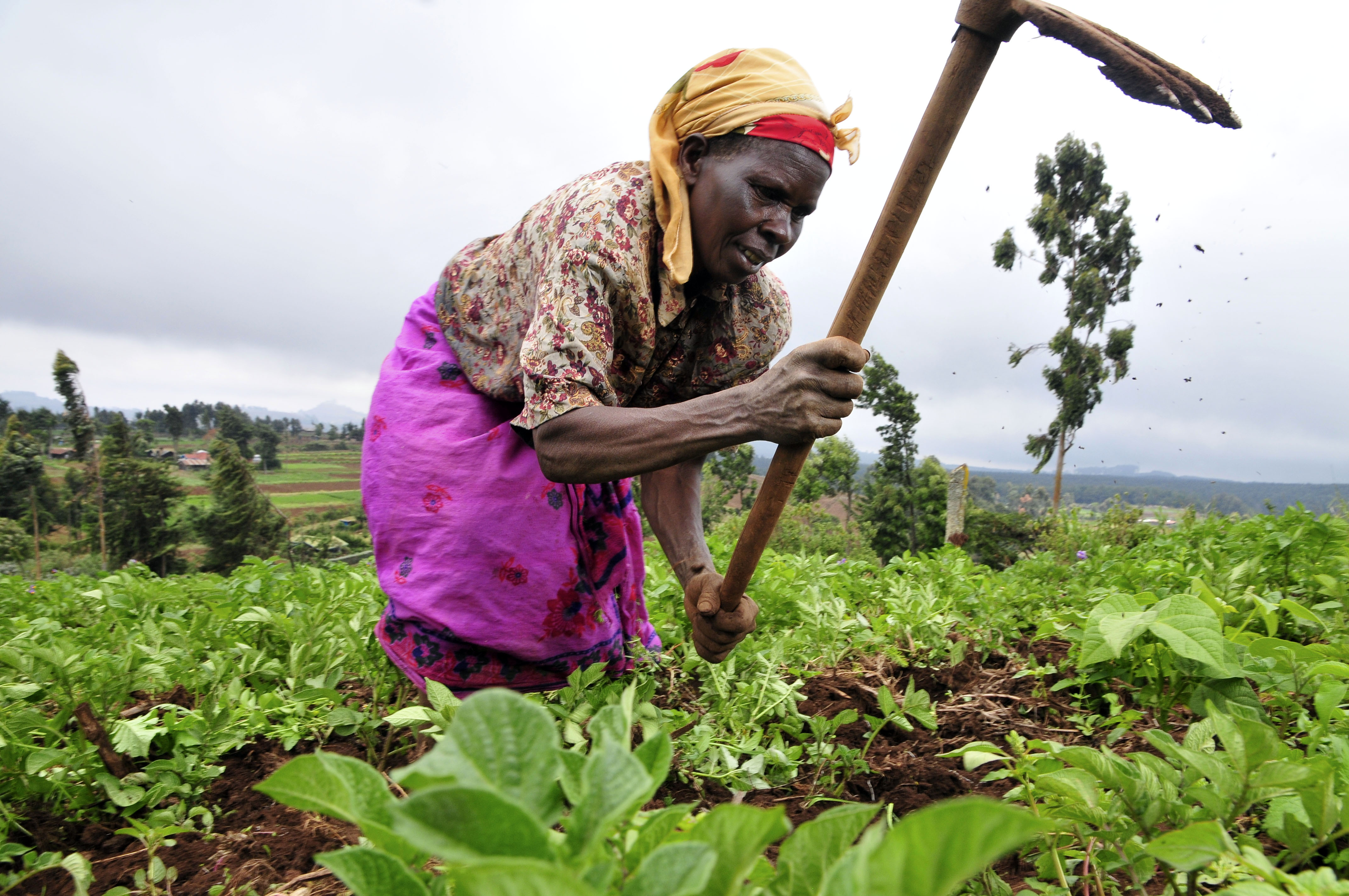
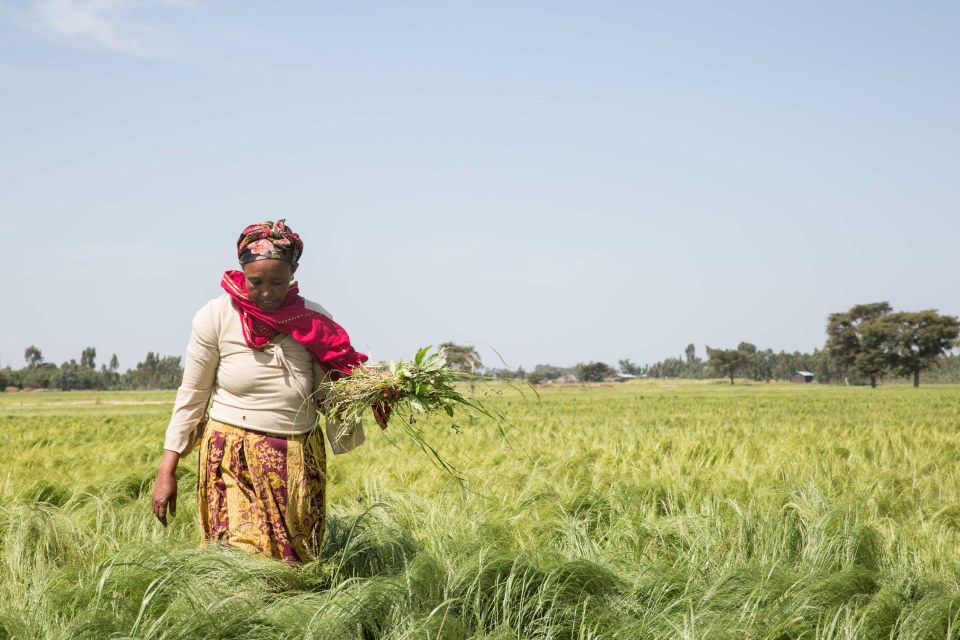
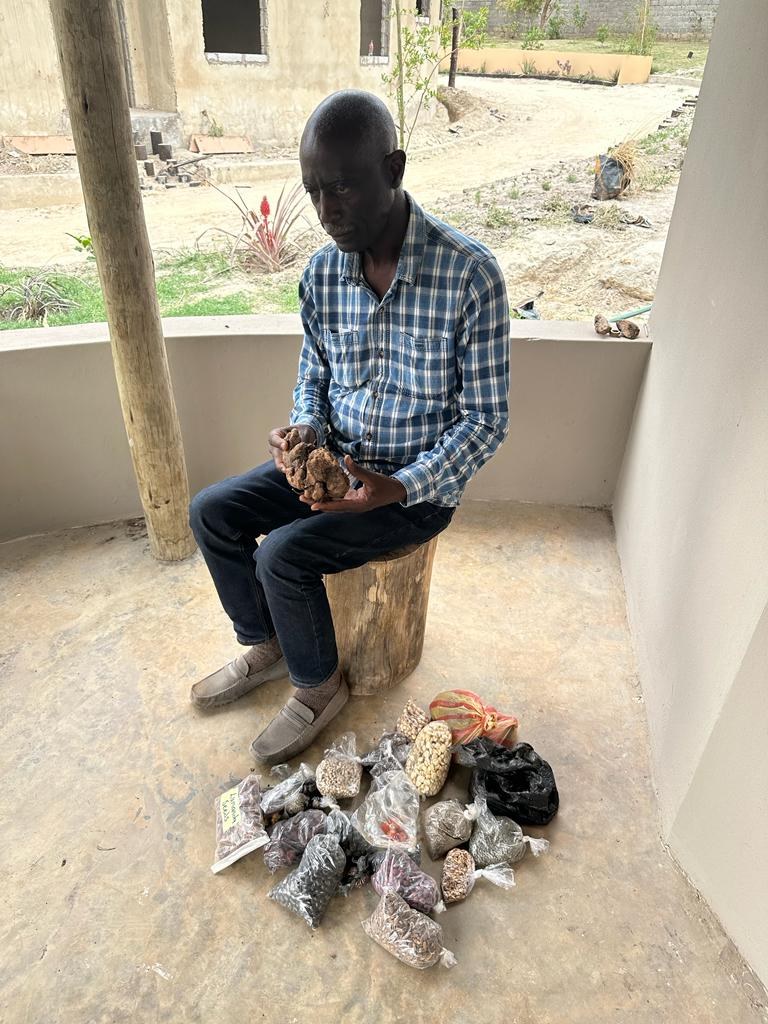
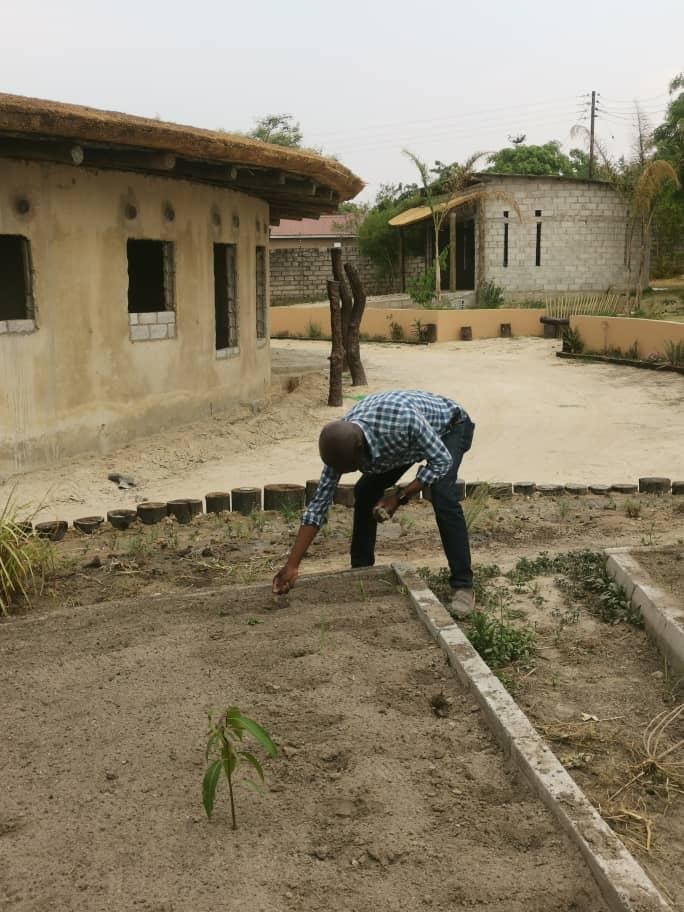
GCNF wishes everyone a Happy New Year and we look forward to continuing to support the world’s children to have the nutrition they need to learn and to thrive in 2024!
Continue readingFree meals for primary school students will be introduced in all schools in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan has made commitments to the well-being of students through national guidelines and free meals for all primary school students.
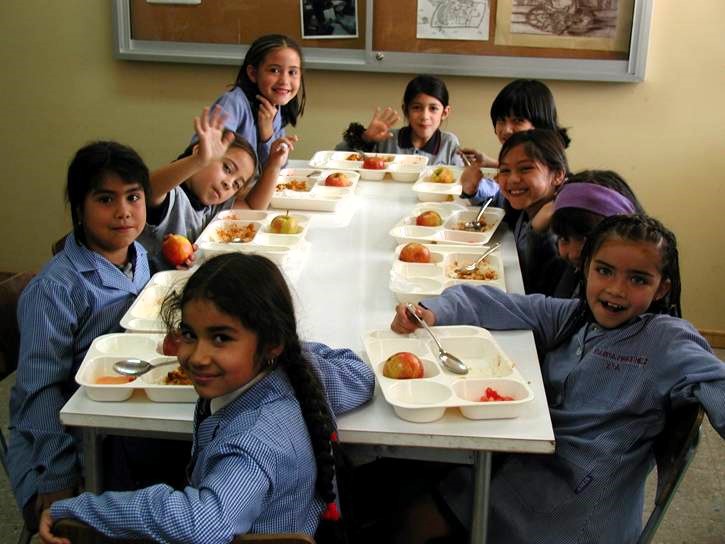
Continue readingCountry Spotlight: Chile
Chile is tackling overnutrition vigorously, and others are paying attention. Read about how the Chile school meal program plays a part.
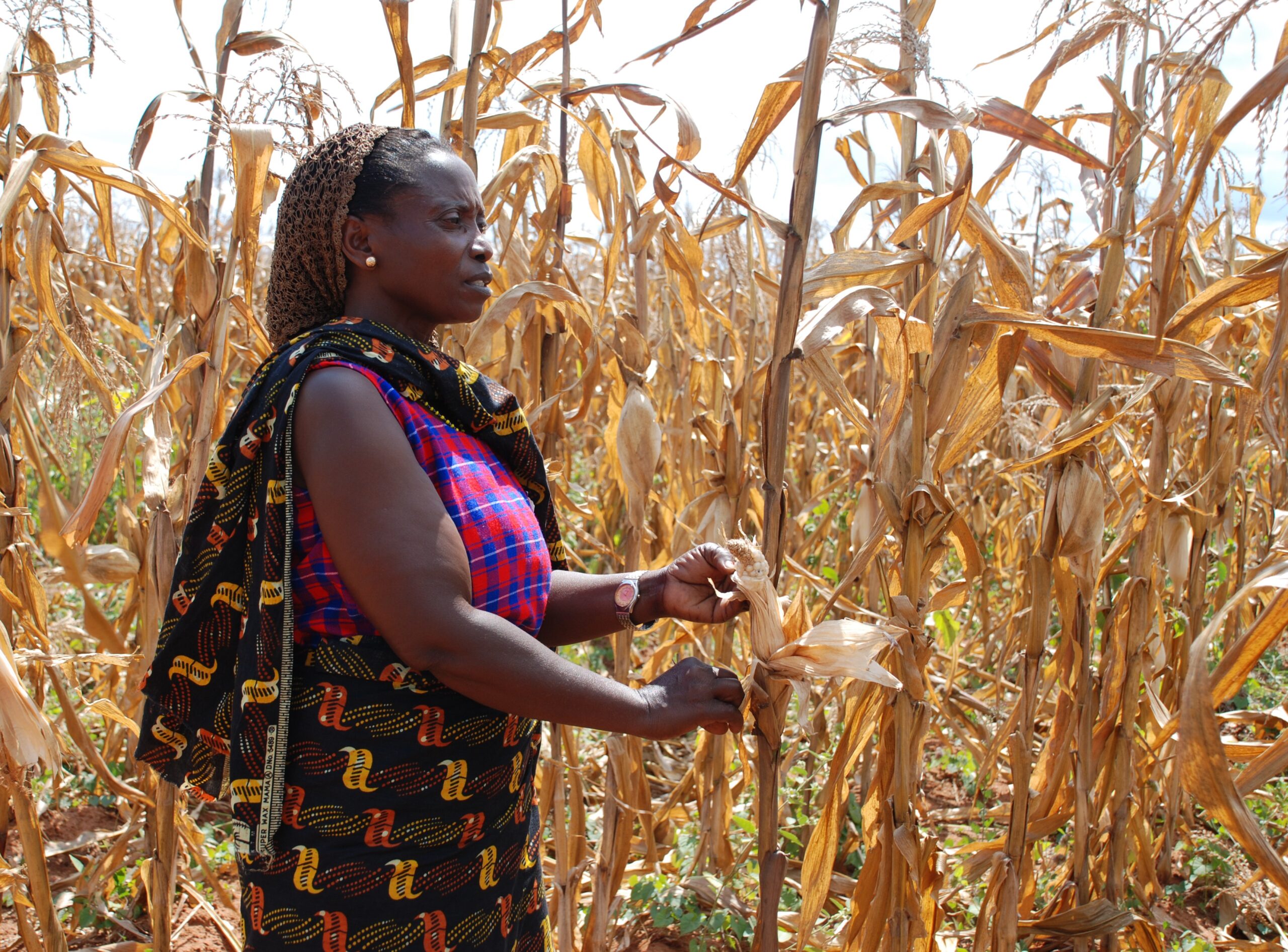
Continue readingCombating Food Insecurity and Promoting Sustainability: School Feeding in Namibia
School feeding programs in Namibia aim to address the challenges of food insecurity and malnutrition among children. These programs provide nutritious meals to students, ensuring they have the energy and nutrients they need to learn and grow.
Continue readingCountry Spotlight: Lithuania
While some countries have a single school meal program that addresses the needs of one identified population, in Lithuania, during the 2020-2021 school year, three different programs took place, reaching over 317,000 pre-, primary, and secondary school students.
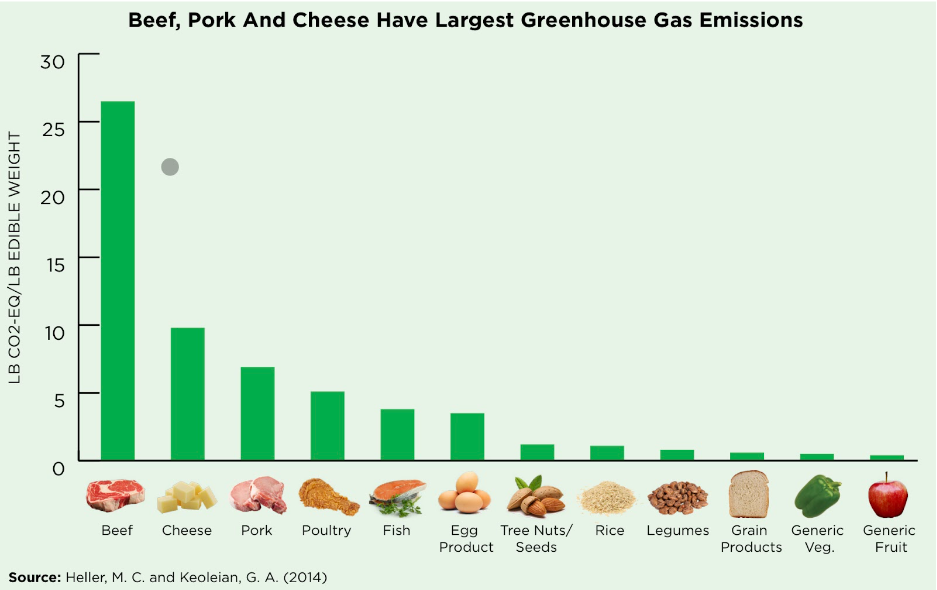
Continue readingClimate-Smart School Meal Programs
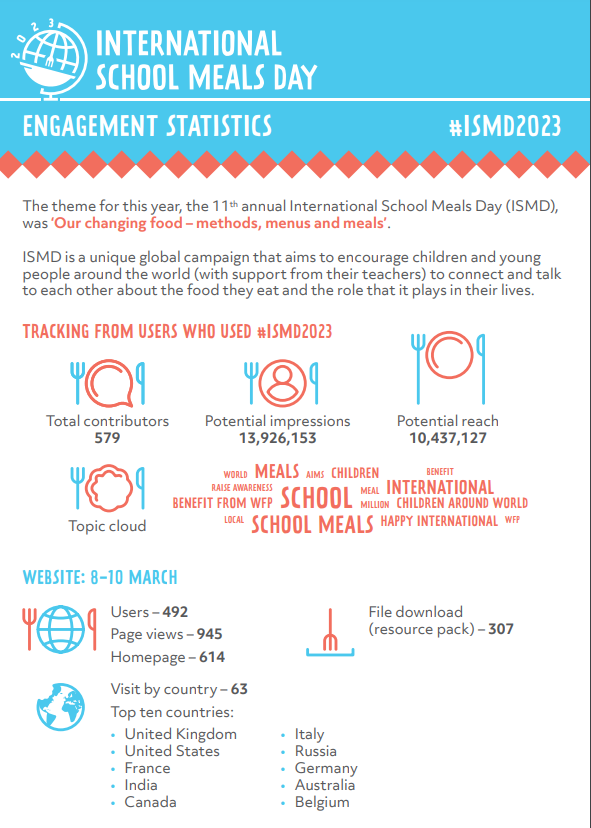
Eleven Years of International School Meals Day
Discussing AUDA-NEPAD Home-Grown School Feeding Guidelines
Home-Grown School Feeding (HGSF) programs aim to provide school children with nutritious meals while also supporting local agriculture and economies. Since the program’s endorsement by the African Union Development Agency New Partnership for Africa’s Development (AUDA-NEPAD) in 2003, the HGSF concept has continued to attract significant attention due to its potential to simultaneously meet various cross-sectoral objectives.
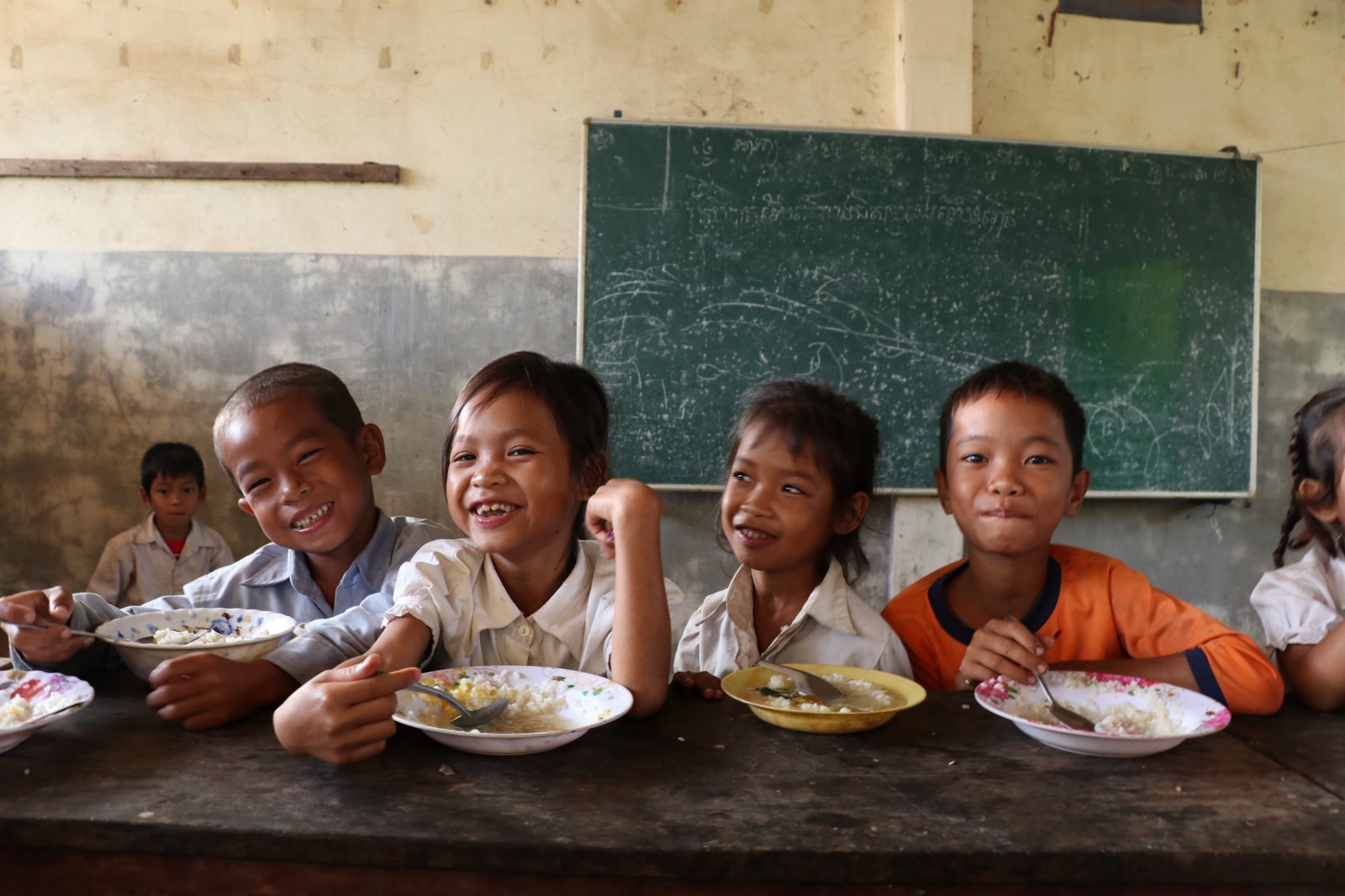
Continue readingGCNF Celebrates International School Meals Day
Every year on March 9, school feeding leaders, government officials, and community members come together to celebrate International School Meals Day. This year, Global Child Nutrition Foundation is celebrating by sharing our top 5 favorite facts about the benefits of school meal programs found around the world.
Continue readingCelebrating International Women’s Day: Women and School Meal Programs
From the United States to Eswatini, and many, many places in between, women form the backbone of many school feeding programs across the globe.
Continue reading